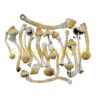
Lion’s mane is a mushroom with a history of both medicinal and culinary uses in Asia and Europe. Medicinal mushroom use dates back to 450 BCE when Greek physician Hippocrates discovered the potential anti-inflammatory properties of fungi as well as its role in wound cauterization, according to a 2017 study in the Journal of Restorative Medicine[1].
Lion’s mane grows on old or dead broadleaf tree trunks. Broadleaf trees shed their leaves seasonally and spread their seeds using a vessel, such as fruit.
Lion’s mane is composed of two parts: the visible fruiting body (the mushroom) and the mycelium, which is the bottom structure that resembles roots. Both the fruiting body and the root-like mycelium contain compounds that offer potential health benefits.















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.